The impedance Z of a circuit is the ratio of the phasor voltage V to the phasor current I, measured in ohms Ω.
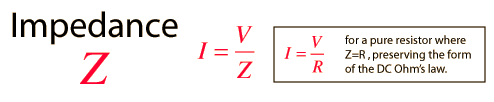
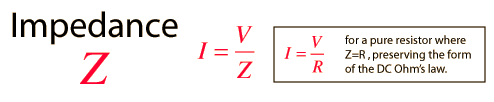
The admittance Y is the reciprocal of impedance, measured in siemens (S).


Formulas Used:

Watch This Videos On How To Solve Impedance and Admittance.

Watch This Videos On How To Solve Impedance and Admittance.
Reflection:
Once you memorize these important formulas, it will be easier for you to convert them which is necessary for solving unknowns in ac analysis. You also need to familiar with them to avoid confusion or interchanging.




